With a choice of ASK, FSK and BPSK you might be wondering about which system you'll most likely see. All other things being equal, BPSK is the best performing system in terms of its ability to ignore noise and so it produces the fewest errors at the receiver. FM is the next best and AM is the worst. On that basis, you'd expect that BPSK is the preferred system. However, it's not necessarily the easiest to implement and so in some situations FSK or ASK might be used as they are cheaper to implement. In fact, FSK was used for cheaper dial-up modems.
To generate a BPSK signal we use the Multiplier module to implement its mathematical model shown in the Fig.1. Digital data for the message is modeled by the Sequence Generator module.
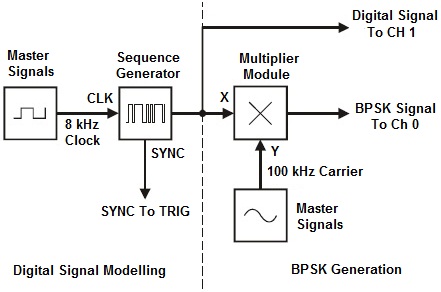 |
In phase shift keying (PSK), the phase of a carrier is changed according to the modulating waveform which is a digital signal. In BPSK, the transmitted signal is a sinusoid of fixed amplitude. It has one fixed phase when the data is at one level and when the data is at the other level, phase is different by 180 °. A Binary Phase Shift Keying ( BPSK ) signal can be defined as
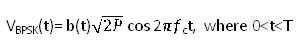 |
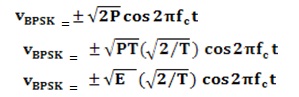 |







