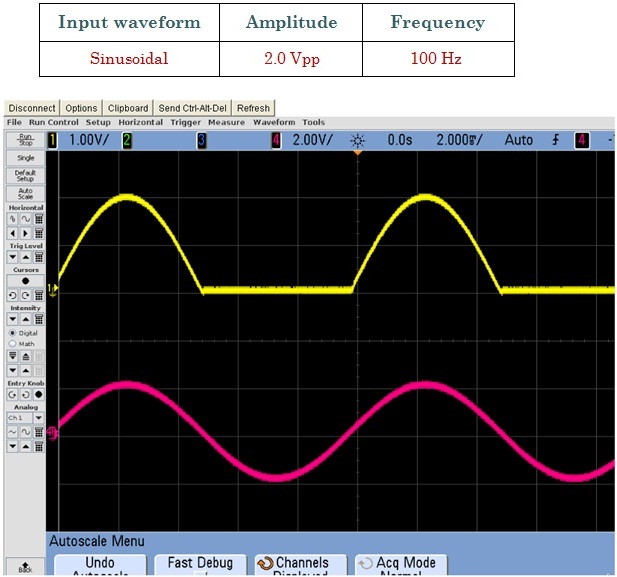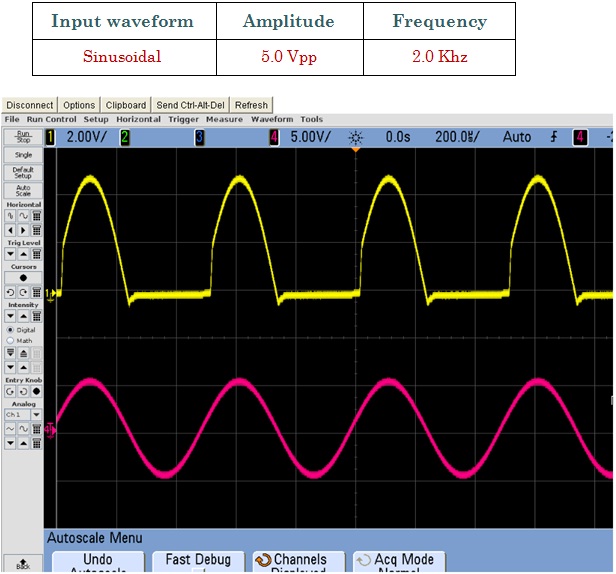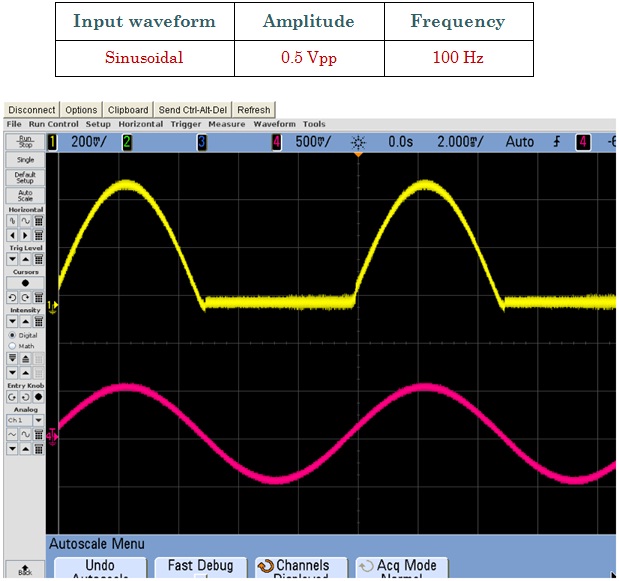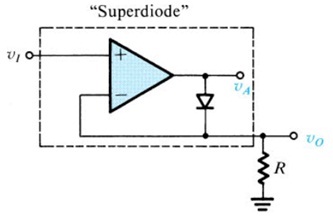
The circuit works as follows: if Vi goes positive, the output VA of the op-amp will go positive and the diode will conduct, thus establishing a closed feedback path between the op-amp’s output and negative input terminal. This negative-feedback path will cause a virtual short circuit to appear between the two input terminals. Thus the voltage at the negative input terminal, which is also the output voltage Vo, will equal (to within a few millivolts) that at the positive input terminal, which is the input voltage Vi